Blockchain Operations
Introduction
The blockchain interaction in CattleChain project is really staright forward, earlier the development was happening using Hyperledger Sawtooth, as sawtooth lack in various aspect and we decided to use the stable/proven blockchain technology.
To do so we are currenlty using Alastria Network, a non-profit association that promotes the digital economy through the development of decentralised ledger technologies/Blockchain and also a member of FIWARE.
Alastria partners have two operational networks (Network T and Network B) on which nodes can be deployed (either regular nodes or critical: validators and bootnodes).
The first of Alastria’s partner node networks (Red T) is built on Quorum technology,an open-source Ethereum client developed under the LGPL license and written in Go. GoQuorum is an Ethereum-based protocol that runs private, permissioned networks.
To know more about it follow here:
- Alastria Network
- Quorum Technology
- GANACHE-CLI (TESTRPC) Test Network for the development.
Use of AEI Contract
CattleChain project using AEI (Asset, Event, Identity) Standard Contract. AEI Smart Contract is written in Solidity using ERC721 standard (NFT) and can be use with Ethereum Clients. It is compatible with FIWARE-Canis Major Adaptor to store the data in blockchain. AEI, asset, events (metadata), identity, is designed to store the NGSI-LD model with the help of Canis Major Adaptor.
ERC 721 Contract is follow OpenZepplin standards, security audits are trusted by leading organizations building decentralized systems.
ERC 721
ERC 721 A standard interface for non-fungible tokens, also known as deeds. The following standard allows for the implementation of a standard API for NFTs within smart contracts. This standard provides basic functionality to track and transfer NFTs.
We considered use cases of NFTs being owned and transacted by individuals as well as consignment to third party brokers/wallets/auctioneers (“operators”). NFTs can represent ownership over digital or physical assets. We considered a diverse universe of assets, and we know you will dream up many more:
Physical property — houses, unique artwork Virtual collectables — unique pictures of kittens, collectable cards “Negative value” assets — loans, burdens and other responsibilities In general, all houses are distinct and no two kittens are alike. NFTs are distinguishable and you must track the ownership of each one separately.
to know more follow here:
AEI Contract Design
AEI contract is cosist of 3 aspects (see the figure below):
- Entity/Asset with a unique identity will be a new asset (1:1 mapping of asset to an identity).
- Event or Metadata of the asset/entity has a 1:n mapping.
- An Asset can have a 1:n relationship with any other asset.
![]()
Example
![]()
To Store the NGSI-LD model there are few possibilities with the help of some supported storage type:
- IPFS
- IOTA MaM
- MerkleRoot
![]()
Methods
- createAsset(bytes32 uuid, string memory _newHash)
- getAsset(bytes32 uuid)
- updateAsset(bytes32 uuid, string memory _newHash)
- removeAsset (bytes32 uuid)
- isValidAsset(bytes32 uuid, bytes32[] memory _proof, bytes32 _leaf)
- isValidAssetEthMessage(bytes32 uuid, bytes32 _messageHash, bytes memory _signature)
- addRelation(bytes32 uuid, bytes32 reluuid)
- getRelations(bytes32 uuid)
- removeRelation(bytes32 uuid, uint index)
- isValidRelation(bytes32 uuid, uint index, bytes32[] memory _proof, bytes32 _leaf)
- addMetadata(bytes32 uuid, string memory _metadatahash)
- getMetadatas(bytes32 uuid) public view returns (string[] memory)
- removeMetadata(bytes32 uuid, uint index)
- isValidMetadata(bytes32 uuid, uint index, bytes32[] memory _proof, bytes32 _leaf)
Apart from that ERC721, Ownable, MerkleProof, ECDSA methods are supported.
Dependencies
This project uses:
- truffle
- NodeJS
- Ganache-CLI (testrpc)
- OpenZeppelin
to know more follow here:
Use of Canis Major
CanisMajor is a blockchain adaptor that supports various DLT.
Canis Major Design
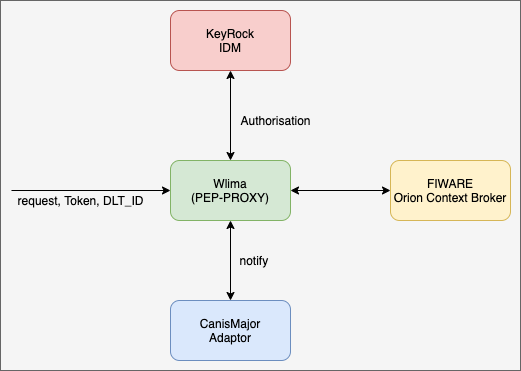
The way Canis Major work's in 'Powered By FIWARE' architecture as follows:
- Request from the user is consist of the Payload, Header with token and DLT_ID (base64 of public key and private key of the blockchain).
- Wilma PEP Proxy validate the token and check with the KeyRock IDM and validate the user, permission (Authentication and Autherisation).
- Once the user is validate Wilma forward the request to the Context Broker and persist it.
- Once the Payload stored in Context Broker Wilma notify to Canis Major with the configuration such as what attribute of the payload should be store, Blockchain Identity of the user.
- Futher Canis Major persist the data in blockchain using AEI contract (will be explained futher in this chapter).
Usages
Creation of an Entity (Animal, Farm etc)
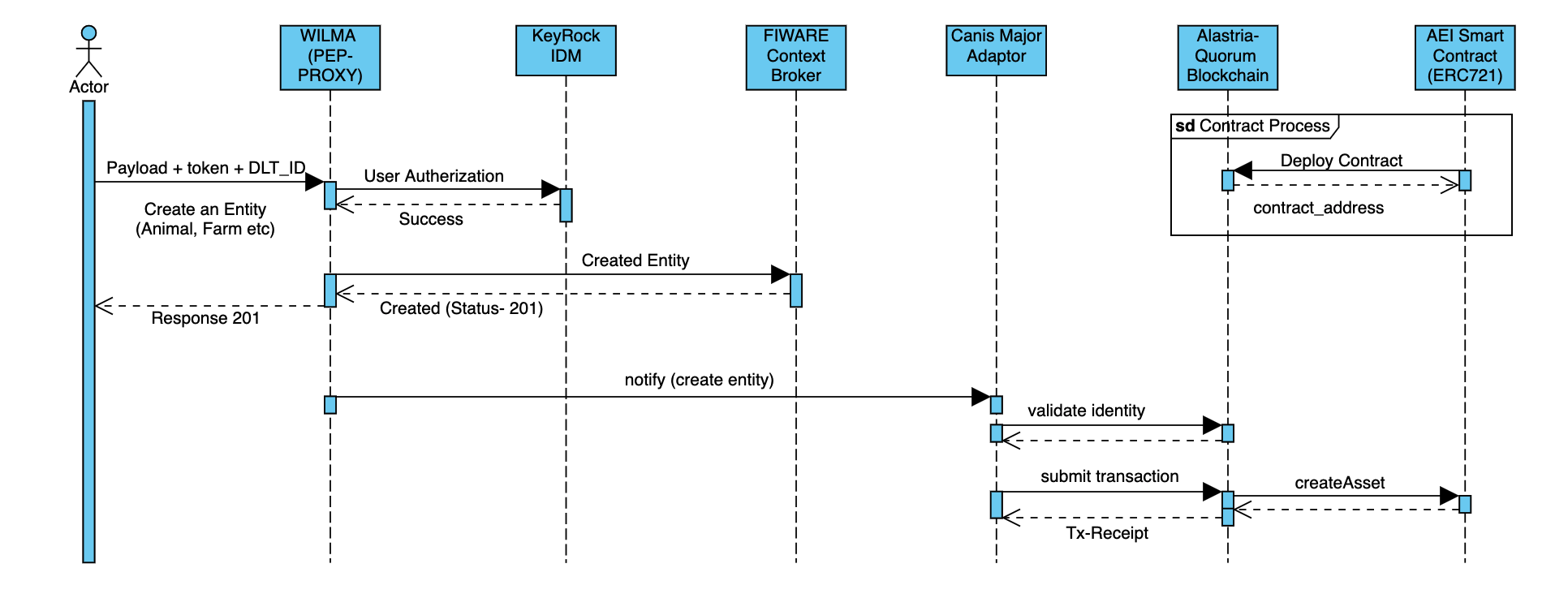
Creation of an entity goes as follow:
- Actor create an request with a payload to PEP Proxy.
- the request is consist of the payload and in header TOKEN (generate from the keyrock IDM) and the DLT_KEYS (which is a base64 for public and private key of the wallet).
- Wilma autherize the request of the user by validating it from the keyrock IDM.
- On Success wilma submit the request to the Context Broker and the entity will be store.
- On Successfully entity creation wilma notify the CanisMajor Adaptor to persist the entity in blockchain (where the smart contract is already configured).
- Willma notify the CanisMajor with payload, dlt_keys in header and it also support option ctx_map (which allow user to mention what particular keys from the payload should be persist in the smart contract).
- Canis Major further validate the DLT_KEY (identity), create a signed transaction and submit it to the blockchain.
- Here we are using AEI_Contract and the createAsset method of the contract is called.
- On successful transacation creation the tx_reciept of the transaction will be available in canis major, which can be queried any time.
Adding Metadata (eventy) on an Entity (Animal, Farm etc)
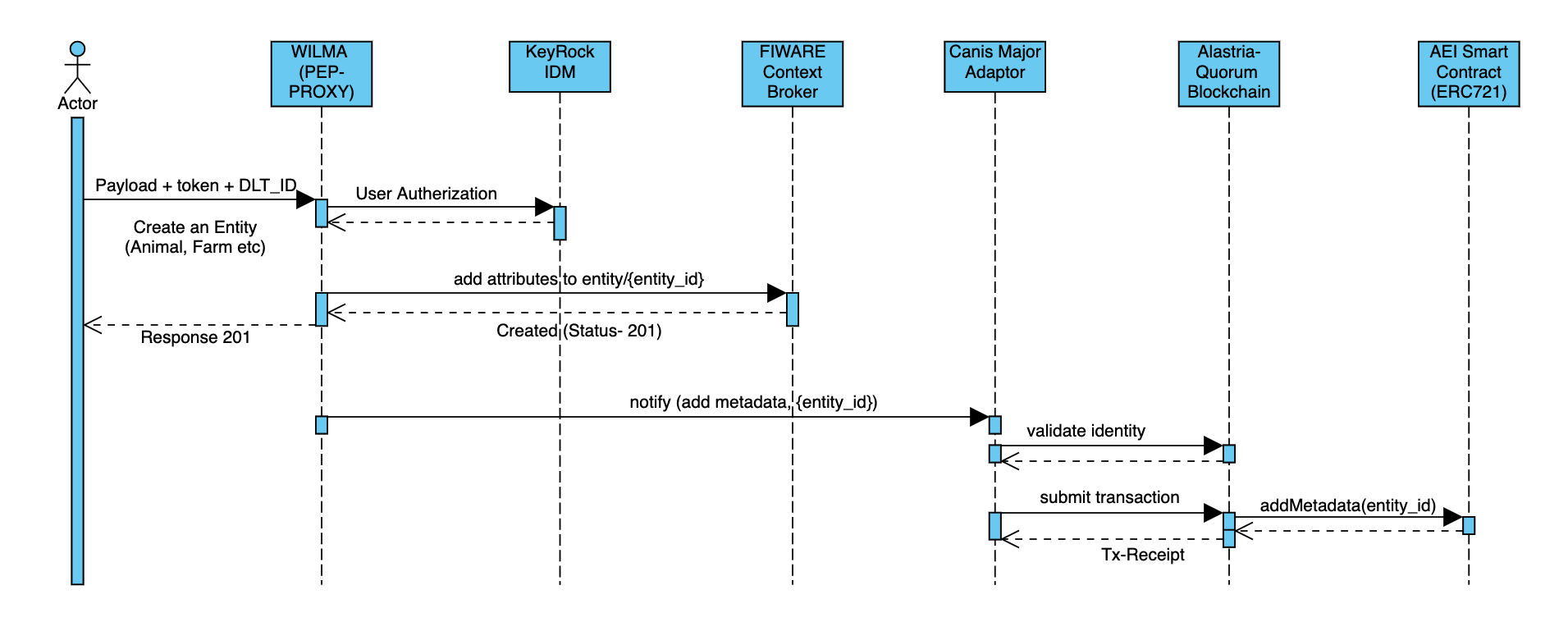
Adding Metadata on an entity goes as follow:
- Actor create an request with a payload to PEP Proxy.
- the request is consist of the payload and in header TOKEN (generate from the keyrock IDM) and the DLT_KEYS (which is a base64 for public and private key of the wallet).
- Wilma autherize the request of the user by validating it from the keyrock IDM.
- On Success wilma submit the request to the Context Broker with the meta information and entity_id.
- On Successfully entity creation wilma notify the CanisMajor Adaptor to persist the entity in blockchain (where the smart contract is already configured).
- Willma notify the CanisMajor with payload, dlt_keys in header and it also support option ctx_map (which allow user to mention what particular keys from the payload should be persist in the smart contract).
- Canis Major further validate the DLT_KEY (identity), create a signed transaction and submit it to the blockchain.
- here the request is for adding the metadata, canis major will call AddMetadata method of the AEI Contract.
- On successful transacation creation the tx_reciept of the transaction will be available in canis major, which can be queried any time.
Qyery
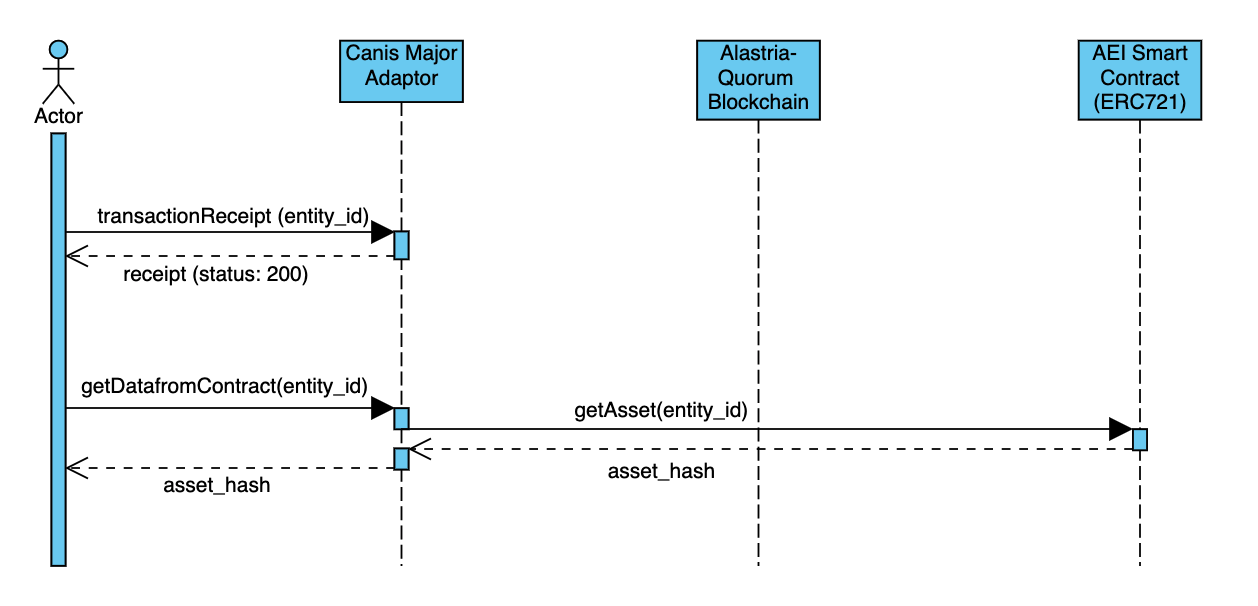
Quering the data on blockchain goes as follow:
- Actor send a request to canis major with the Entity_ID.
- Canis major check the transaction details from the local storage and fetch the reciept.
- Canis Major futher call the AEI contarct, getAsset method and the fetch the stored hash.
- Hash will be returned back to the hash.
**Note: the returned Hash could be a IPFS Hash, IOTAMaM hash or MerkleRoot, depend on the configuration of the CanisMajor and data from the has can be fetched or validated from the canismajor query apis (for more checkout the canismajor api specification)"